In today’s interconnected world, safeguarding network infrastructure is crucial. Network scanning techniques play a vital role in identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring robust security. This guide delves into various network scanning methods, their significance, and practical applications.
What Is Network Scanning?
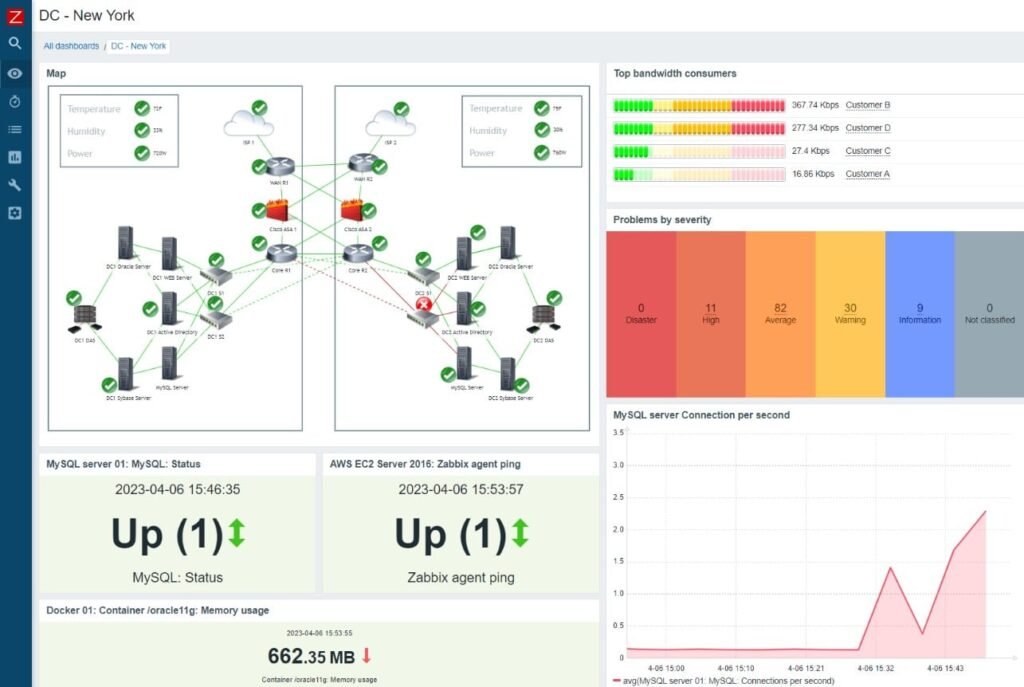
Network scanning involves systematically examining a network to discover active devices, open ports, and potential vulnerabilities. It’s a fundamental aspect of network security, aiding administrators in assessing the health and security of their system.
- Identifying Vulnerabilities: Detects weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors.
- Network Inventory: Provides a comprehensive list of devices connected to the network.
- Performance Assessment: Helps in evaluating network health and efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assists in meeting security standards and regulations.
Importance of Network Scanning
Common Network Scanning Techniques
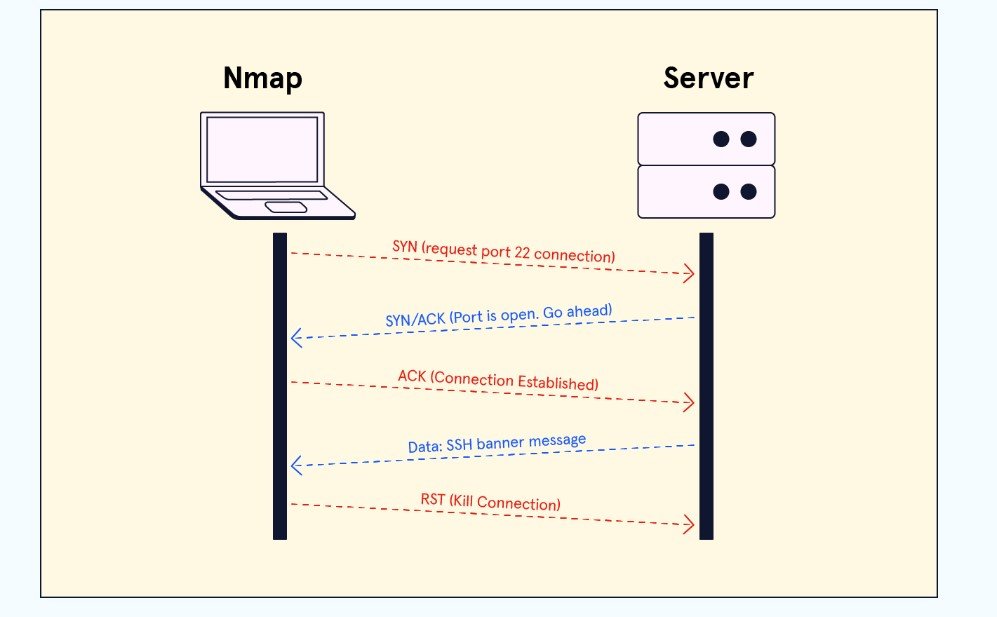
1. Port Scanning
Port scanning identifies open ports and services on a host, revealing potential entry points for attacks. Common port scanning methods include:
- SYN Scan: Also known as half-open scanning, it sends SYN packets to detect open ports without completing the TCP handshake, making it stealthier.
- XMAS Scan: Sends packets with specific flags set, identifying open ports based on responses. It’s less commonly used due to its detectability.
2. Vulnerability Scanning
This technique assesses systems for known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and outdated software, providing insights into potential security risks.

3. Network Vulnerability Scanning
Focuses on identifying vulnerabilities within the network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and firewalls, ensuring the overall security of the network.
4. Ping Sweep (ICMP Scanning)
Ping sweeps determine active devices within a network by sending ICMP echo requests to multiple hosts and analyzing the responses.
5. Protocol Scanning
Identifies active protocols on a network, such as TCP, UDP, and GRE, providing insights into the types of traffic and services in use
How to Perform Network Scanning
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline the purpose of the scan, whether it’s for vulnerability assessment, compliance, or routine maintenance.
- Select Appropriate Tools: Choose tools that align with your objectives. Popular options include Nmap for port scanning and Nessus for vulnerability assessments.
- Conduct the Scan: Execute the scan during maintenance windows to minimize disruption, ensuring all relevant devices and IP ranges are included.
- Analyze Results: Review the findings to identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, or unauthorized devices.
- Implement Remediations: Address identified issues promptly to enhance network security.
Best Practices for Network Scanning
- Regular Scanning: Perform scans periodically to detect new vulnerabilities or unauthorized changes.
- Update Scanning Tools: Ensure tools are up-to-date to recognize the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
- Maintain Documentation: Keep detailed records of scans, findings, and remediation actions for future reference and compliance purposes.
- Obtain Proper Authorization: Always have explicit permission before scanning networks to avoid legal and ethical issues.

