In today’s digital age, securing your operating system (OS) is crucial to protect your data and ensure smooth functioning. Cyber threats are evolving, and a poorly protected OS can leave your personal or professional information vulnerable. This guide provides essential tips on how to secure your operating system effectively.
Keep Your Operating System Updated:
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to secure your OS is by keeping it updated. Regular updates include security patches that fix vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of cyberattacks.
Why Updates Matter:
- Security Patches: Fixes for newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Performance Improvements: Enhances overall system stability.
- Compatibility Fixes: Ensures smooth functioning with new software or hardware.

Pro Tip: Enable automatic updates to ensure you never miss critical security patches.
Install and Regularly Update Antivirus Software
Antivirus software acts as the first line of defense against malware, viruses, and other threats.
Features to Look For:
- Real-Time Protection: Monitors and blocks threats as they occur.
- Frequent Updates: Ensures protection against the latest threats.
- Customizable Scans: Lets you target specific areas of your system.
Pro Tip: Choose a reputable antivirus program and schedule regular full-system scans.
Enable a Firewall:
A firewall acts as a barrier between your computer and potential cyber threats, monitoring and controlling network traffic.
Types of Firewalls:
- Hardware Firewall: Often built into routers, provides network-level security.
- Software Firewall: Integrated into most operating systems; blocks unauthorized access.
How to Enable Your Firewall:
- Navigate to your OS settings.
- Find the security section.
- Ensure the firewall is activated.
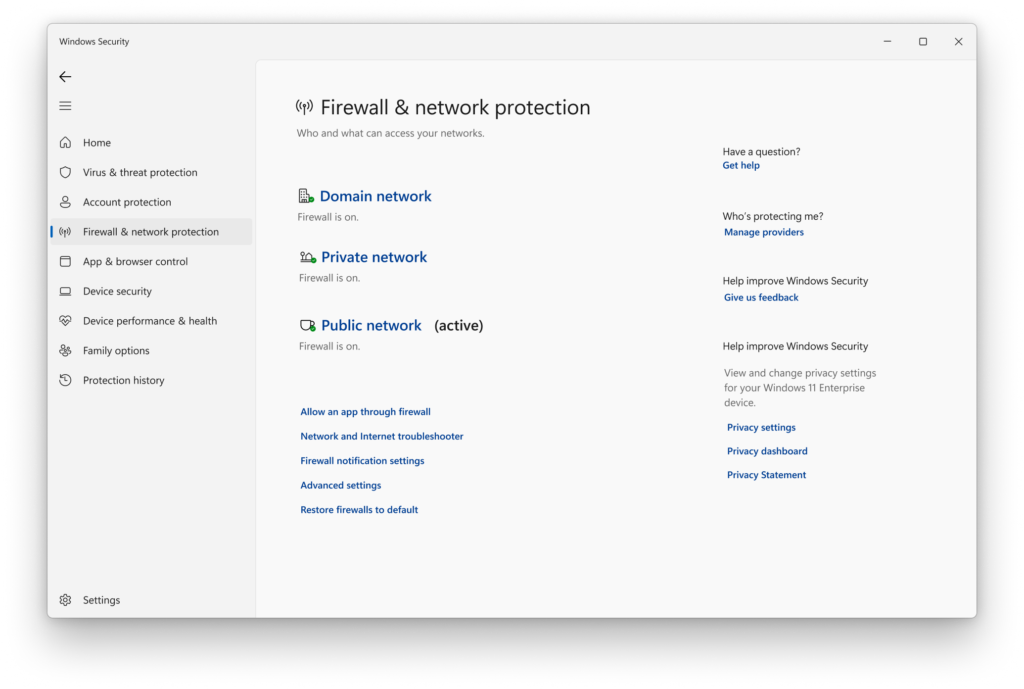
Pro Tip: Pair your firewall with antivirus software for comprehensive protection.
Use Strong Passwords and Authentication:
A strong password is a simple yet highly effective way to secure your OS. Combine it with multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced protection.
Password Best Practices:
- Use a combination of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid easily guessable passwords like “123456” or “password.”
- Change your password regularly.
Multi-Factor Authentication:
- Adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password.
- Common methods include SMS codes, email verification, or biometric authentication.
Limit Admin Privileges:
Limiting admin privileges reduces the risk of unauthorized changes to your system. Create a separate user account for everyday tasks.
Why It Matters:
- Prevents accidental changes to critical system files.
- Minimizes damage if your account is compromised.
Pro Tip: Only log in as an administrator when necessary.
Be Cautious with Downloads and Emails:
Many threats originate from malicious downloads or phishing emails. Practice caution when downloading files or clicking on links.

Safe Download Practices:
- Download software only from official or reputable sources.
- Verify the file size and checksum before installation.
Email Security Tips:
- Avoid clicking on links from unknown senders.
- Look for spelling errors and suspicious email addresses.
Pro Tip: Use email clients with built-in phishing detection.
Backup Your Data Regularly:
Even with the best security measures, data loss can happen. Regular backups ensure you can recover your important files in case of an attack or hardware failure.
Backup Options:
- Cloud Storage: Automatic backups with remote accessibility.
- External Drives: Reliable for offline backups.
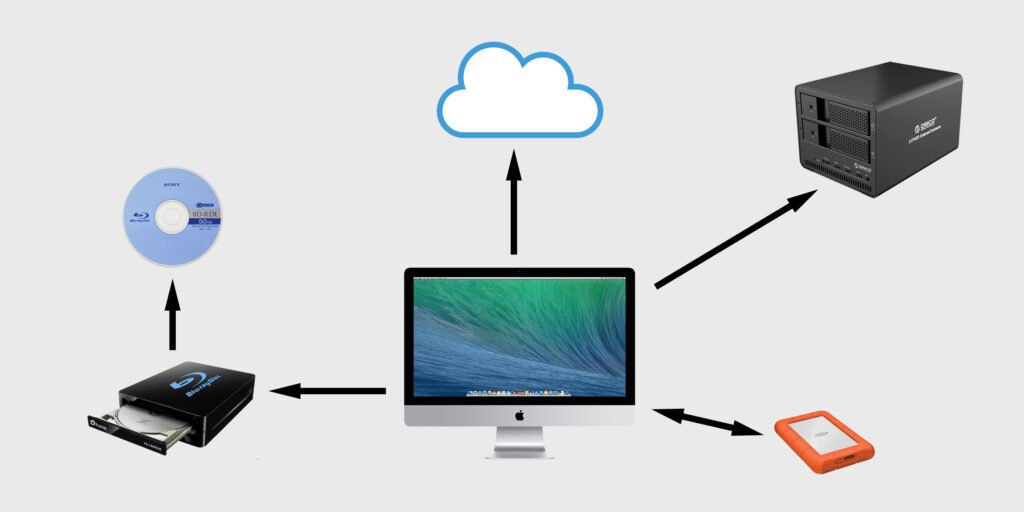
Pro Tip: Schedule weekly backups and test the restore functionality.
Conclusion:
Securing your operating system is not optional—it’s essential. By keeping your OS updated, using antivirus software, enabling a firewall, and following these tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats. Protect your digital life by taking proactive steps today.

